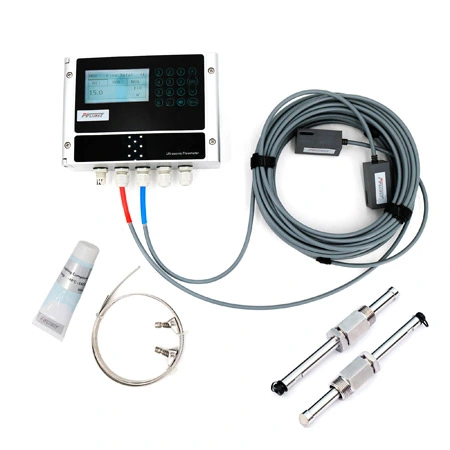
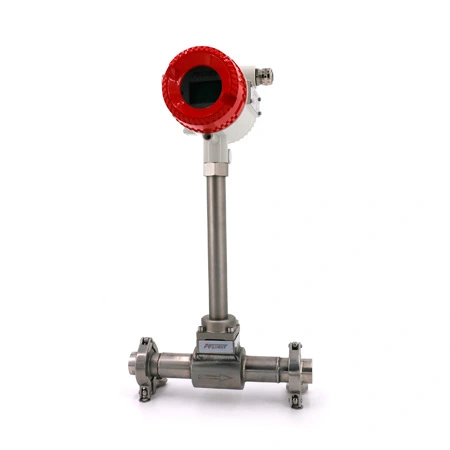
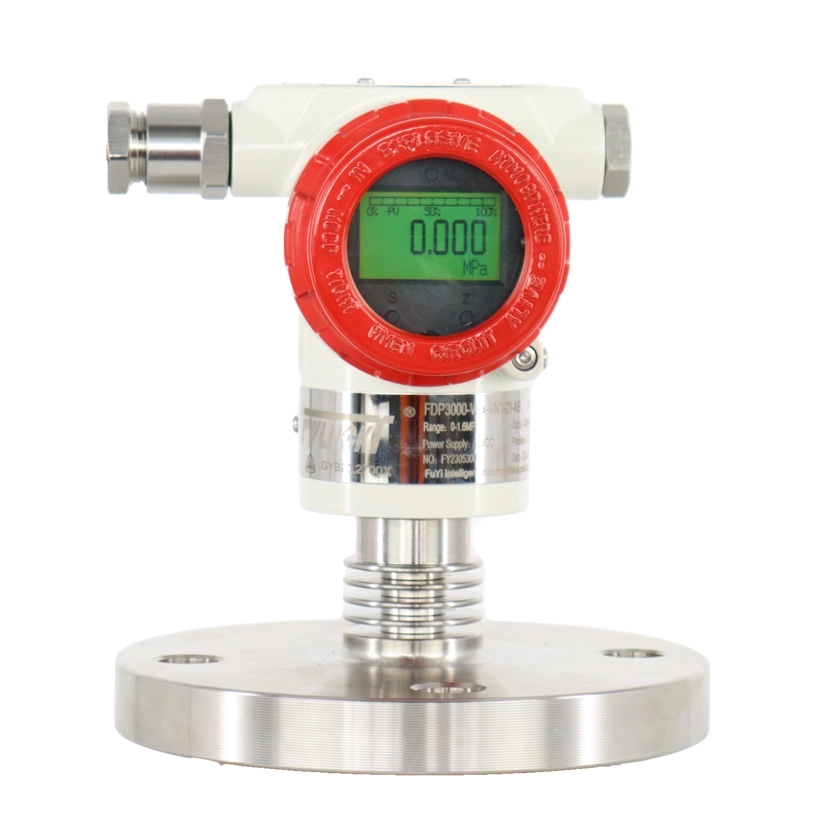
The temperature transmitters working principle profoundly affects the accuracy and efficiency of temperature measurements. This article will delve into the working principles of temperature transmitters, revealing their internal mechanisms and wide-ranging applications across various industries.
A Brief Introduction to the Temperature Transmitters Working Principle
Temperature transmitters—whose functionality aligns with the temperature transducer working principle—as critical devices in the field of industrial automation, are responsible for converting signals from temperature sensors into standardized output signals so that remote monitoring and control systems can accurately read and process the temperature information. Their high precision, stability, and broad applicability make them indispensable measurement tools in many fields, including industrial production and environmental monitoring. The reliability of temperature transmitters directly stems from the maturity of the temperature transmitter working principle, ensuring consistent performance in diverse industrial automation scenarios.
Temperature Measurement Principle: Thermal Equilibrium and High Precision
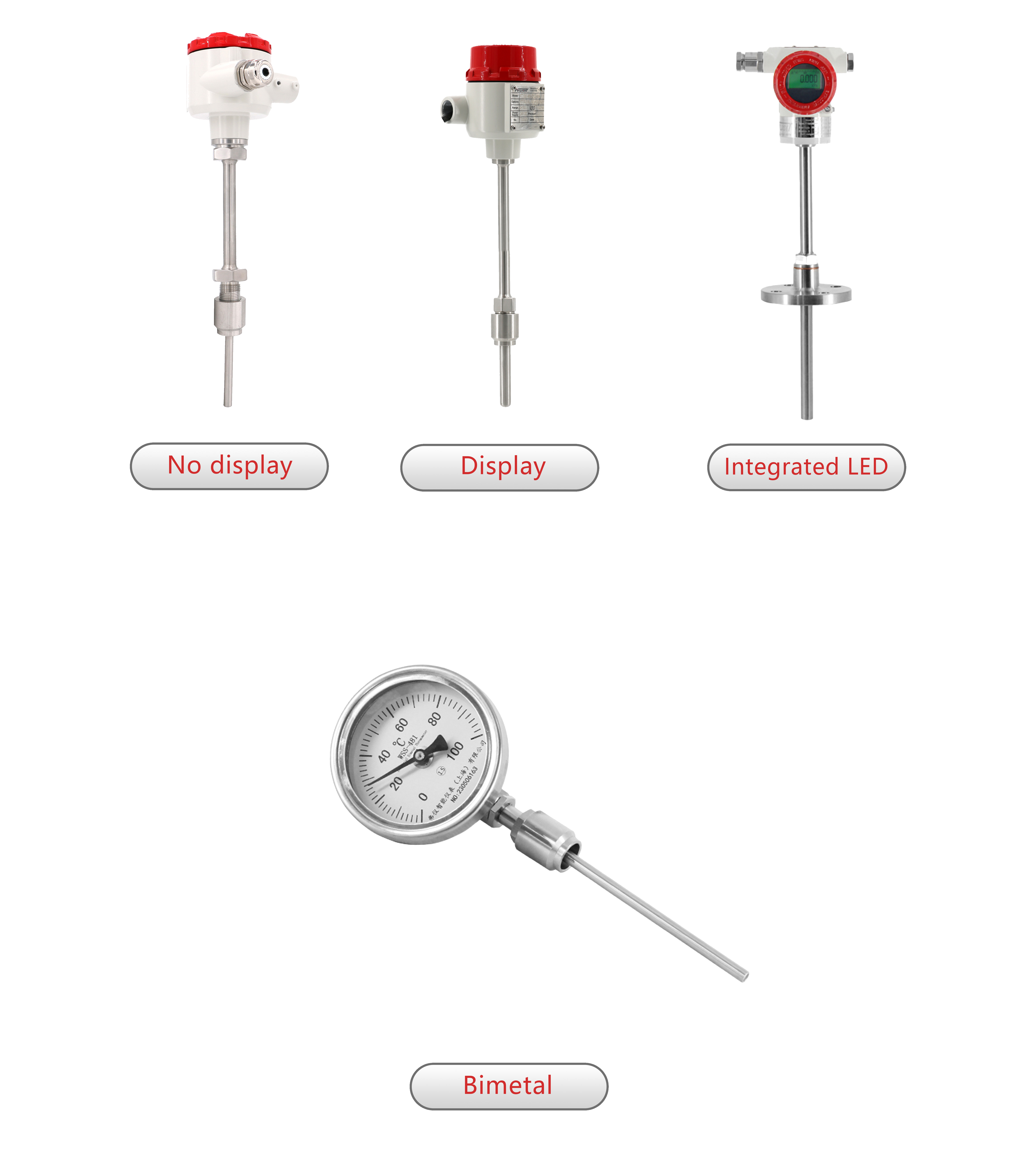
The core of the temperature transmitters working principle lies in their temperature measurement probes, which are usually thermocouple or resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) and this forms the basis of the temperature transmitter function.. These sensors achieve thermal equilibrium with the object being measured through conduction or convection, allowing the temperature gauge's readings to directly reflect the actual temperature of the measured object. This process ensures high precision in measurements, making it particularly suitable for scenarios with stringent temperature control requirements. Additionally, within specific temperature ranges, thermometers can reveal the internal temperature distribution of objects, providing essential data support for process optimization—further validating the practical value of the temperature transducer working principle in industrial applications.
Structural Composition: Integrated Design
Another important temperature transmitters working principle involves their sophisticated structural design, integrating the temperature probe with a two-wire solid electronic unit to form a unified transmitter—an innovative design core to the temperature transmitter working principle. This design not only simplifies the installation process but also enhances the stability and reliability of the equipment. The temperature probe is directly installed within the junction box, effectively preventing external interference and improving measurement accuracy and stability.
Application Areas of Temperature Transmitters
Thanks to their superior performance and extensive application range, temperature transmitters play a crucial role in many sectors including industry, agriculture, and commerce. In industrial production, they are used to monitor and control temperature changes during the production process, ensuring product quality and production safety. In agriculture, temperature transmitters assist farmers in accurately managing the temperature conditions of environments such as greenhouses and farms, optimizing conditions for crop growth and animal breeding. In the commercial sector, such as cold chain logistics and food processing, temperature transmitters are vital for ensuring product quality and safety.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the temperature transmitters working principle is what transforms a simple temperature reading into the actionable, trustworthy data that drives modern industrial automation. This combination of scientific precision and smart engineering is critical for efficiency and safety across countless sectors. FVLUOKY is dedicated to perfecting this principle in every device we manufacture. If you demand unparalleled accuracy and durability for your operations, discover how our advanced temperature transmitters can elevate your process control today.
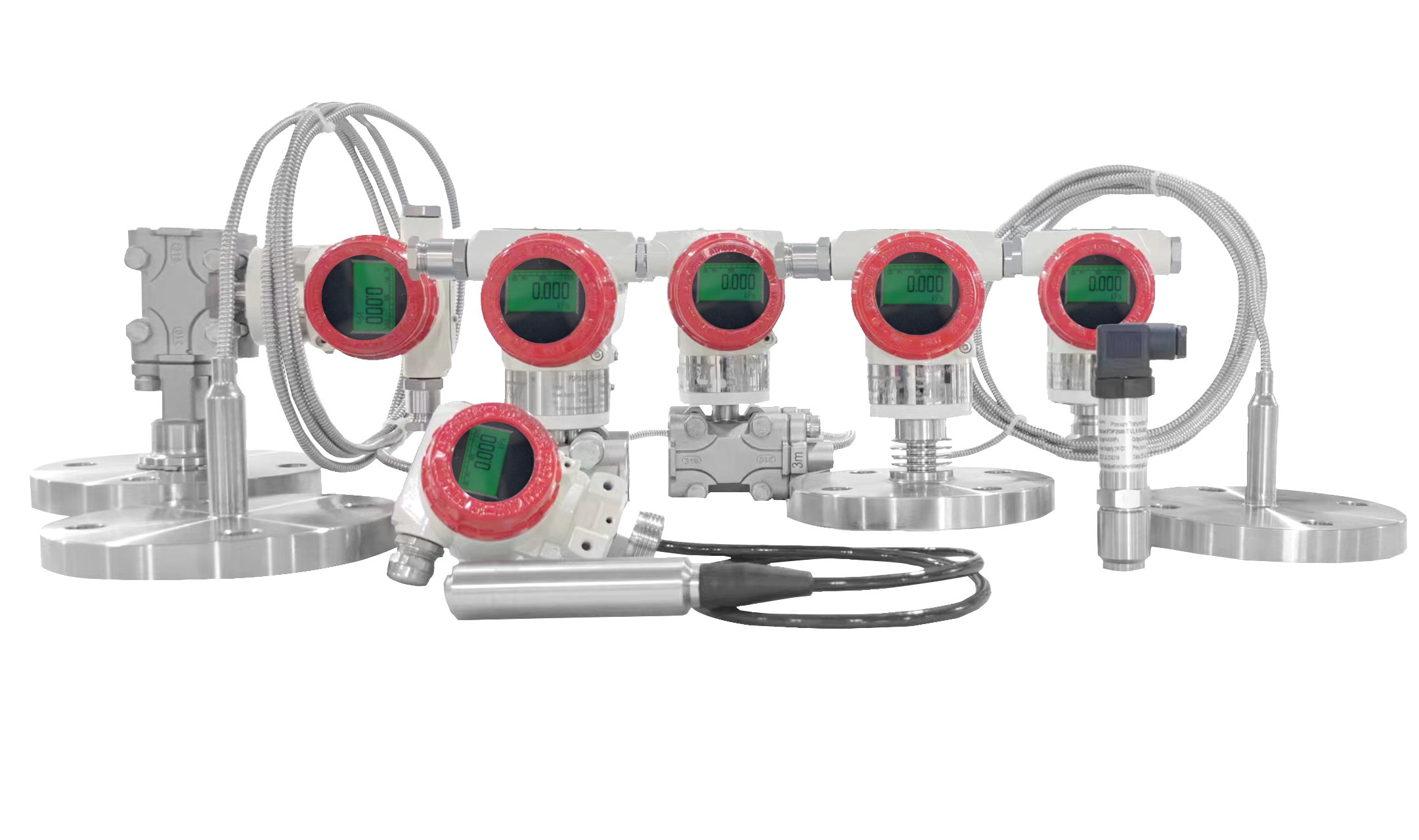
 Smart Pressure Transmitters
Smart Pressure Transmitters