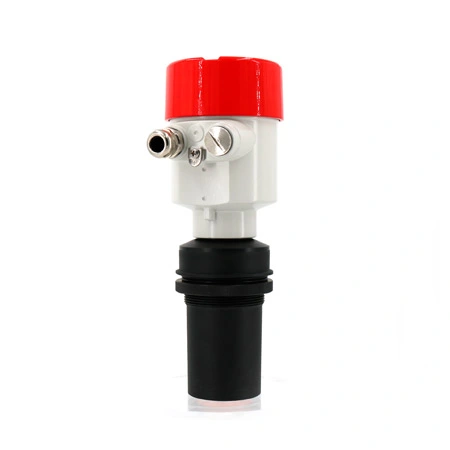
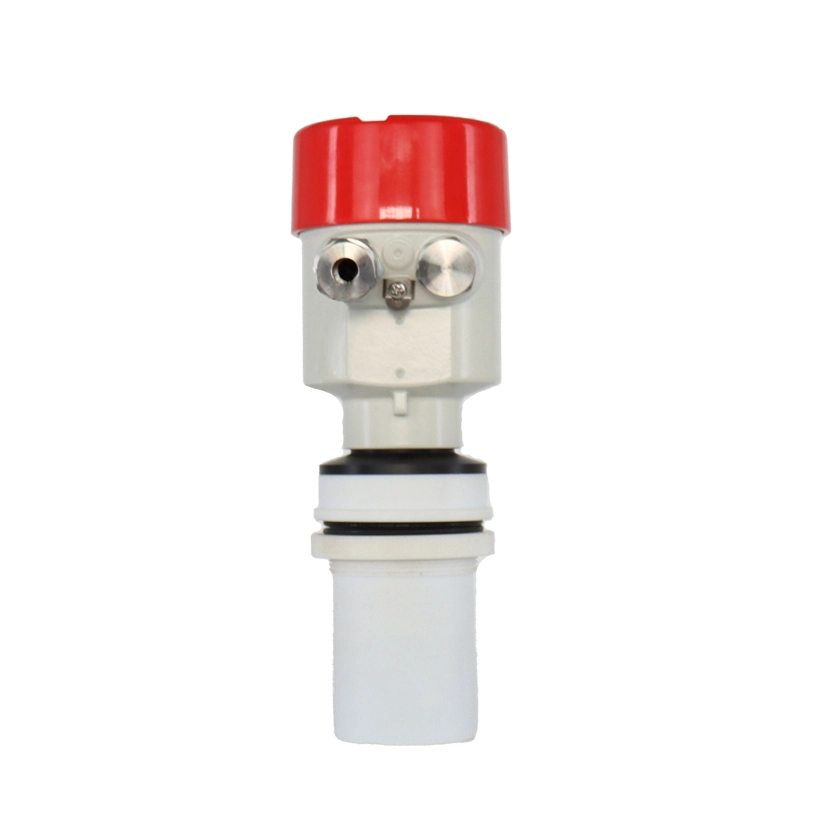
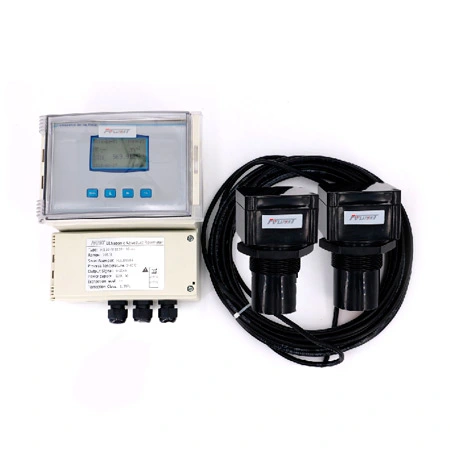
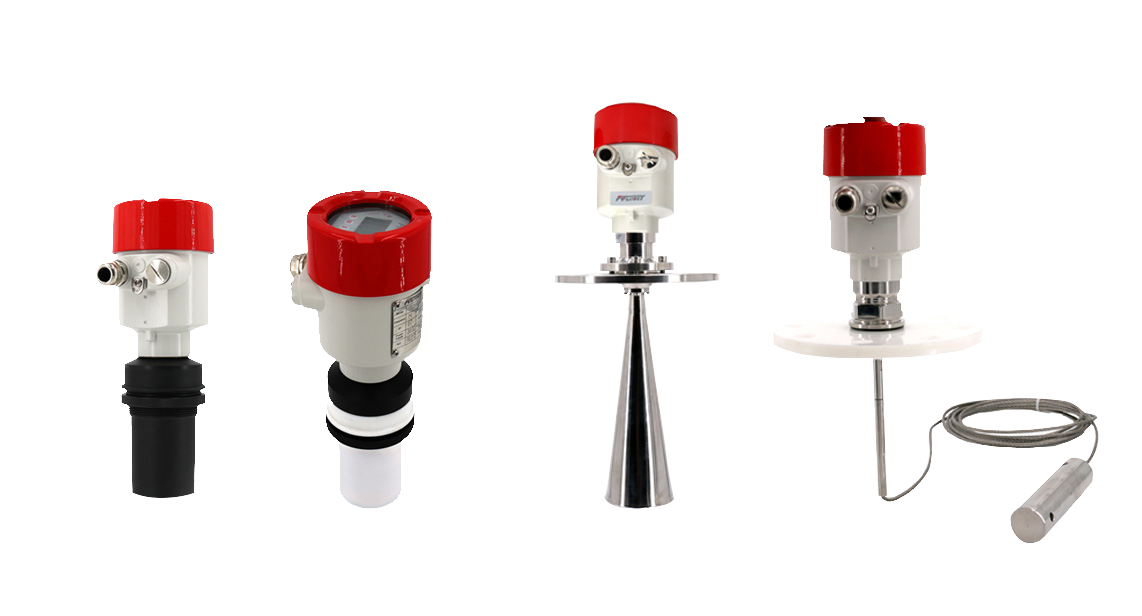
Ultrasonic Level Meters
Ultrasonic level meters utilize sound waves to measure the distance to a surface, typically of liquids or solids, within a container. They offer non-contact, accurate level measurement, ideal for various industrial applications.
How Does A Ultrasonic Level Meters Work?
Ultrasonic level meters operate based on the principle of using sound waves to measure the distance to the surface of a material (liquid or solid) within a container or open space. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how they work:
1. Emission of Ultrasonic Pulses:
The device, equipped with an ultrasonic transducer, emits high-frequency sound waves (ultrasonic pulses) towards the surface of the material whose level is being measured. These sound waves are typically in the frequency range of 20 kHz to 200 kHz, which is above the audible range of human hearing.
2. Travel and Reflection of Sound Waves:
The ultrasonic pulses travel through the air and, upon reaching the surface of the material, are reflected back towards the transducer. The nature of the material (liquid, solid, or granular) can affect the strength of the reflected signal but does not significantly hinder the measurement process.
3. Reception of the Echo:
The same transducer that emitted the ultrasonic pulses also acts as a receiver for the reflected sound waves (echo). The time interval between the emission of the sound pulse and the reception of the echo is measured very accurately.
4. Calculation of Distance:
Using the time it took for the echo to return and the known speed of sound in air (which can vary with air temperature), the ultrasonic level meter calculates the distance from the transducer to the surface of the material. This calculation typically uses the formula: Distance = (Speed of Sound in Air x Time) / 2. The division by 2 accounts for the fact that the sound wave travels to the material surface and back.
5. Determination of Level:
To determine the level of the material within the container, the device subtracts the measured distance from the total height of the container. If the container’s dimensions are known and programmed into the device, it can also calculate the volume of the material present.
Key Features and Advantages:
Non-Contact Measurement: Ultrasonic level meters do not need to touch the material they are measuring, making them suitable for corrosive, hot, or otherwise challenging materials.
Versatility: They can measure levels of liquids, solids, and slurries in various types of containers, including tanks, silos, and open channels.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Since they mount on the top of the container and do not contact the material, installation and maintenance are relatively straightforward.
Considerations:
Air Conditions: The speed of sound in air can be affected by temperature, humidity, and pressure, which may need to be accounted for in precise applications.
Obstructions and Beam Angle: The presence of ladders, agitators, or other internal structures can interfere with the sound waves. The device’s beam angle also needs to be considered to ensure accurate measurement.
Ultrasonic level meters are a reliable and widely used technology for level measurement in various industries, including water treatment, chemical manufacturing, and food processing, due to their non-invasive nature and versatility.
How Accurate Is The Ultrasonic Level Measurement?
The accuracy of ultrasonic level measurement can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the equipment, environmental conditions, and the characteristics of the material being measured. Generally, high-quality ultrasonic level meters can achieve accuracy within ±0.25% to ±1% of the measured range. However, this can be influenced by the following factors:
In summary, while ultrasonic level measurement is a versatile and widely used method, its accuracy is contingent upon a variety of factors. Understanding and mitigating these factors can help ensure that ultrasonic level meters perform within the expected accuracy range for a given application.
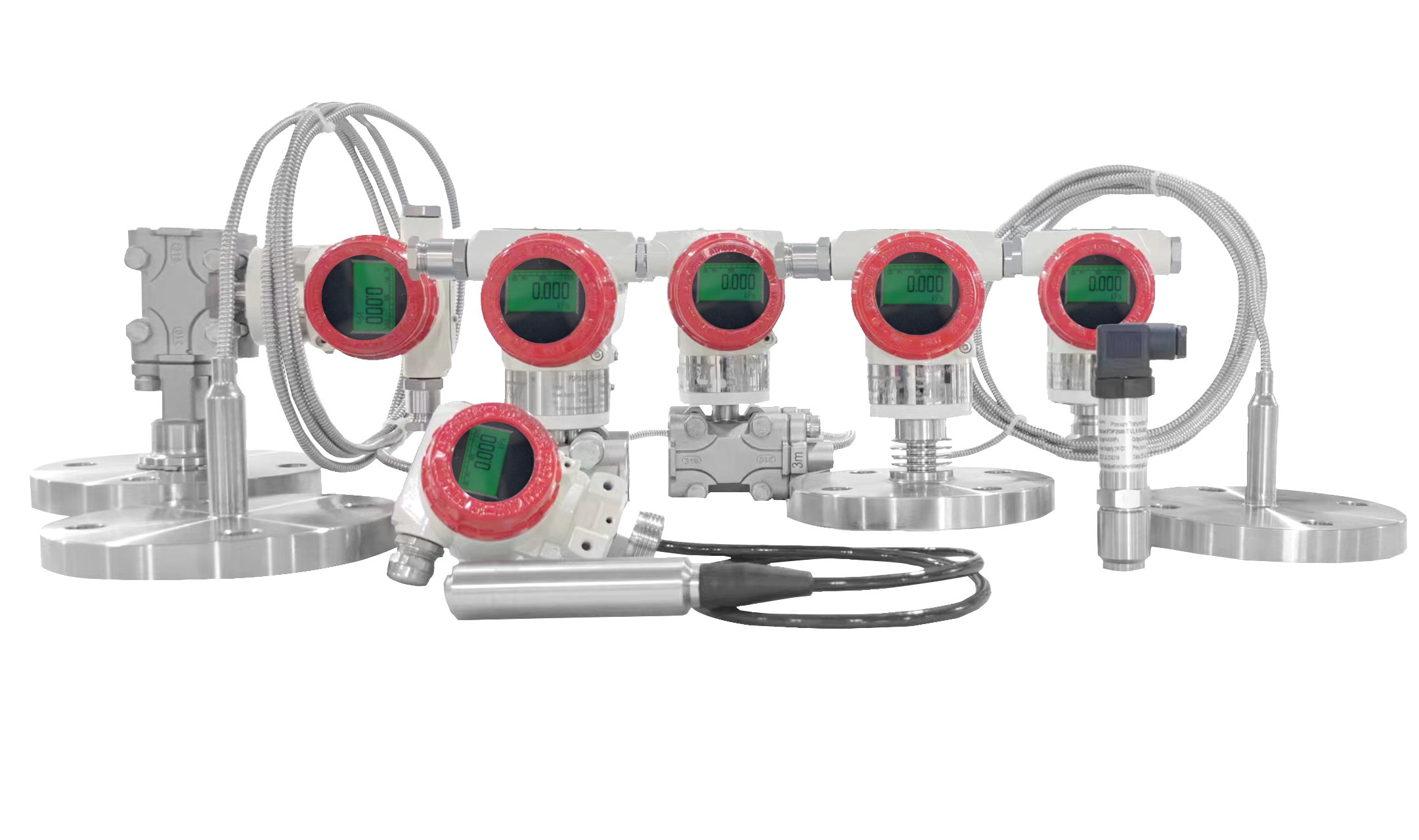
 Smart Pressure Transmitters
Smart Pressure Transmitters