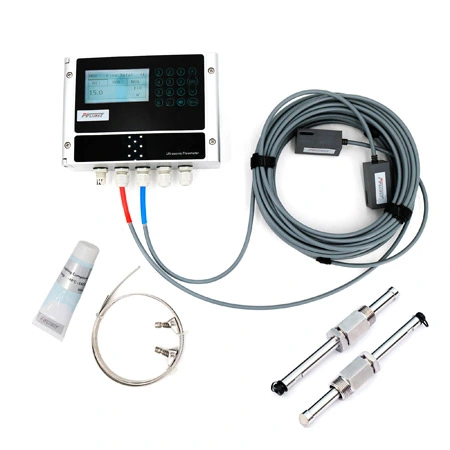
Ultrasonic Flowmeters
Ultrasonic flowmeters measure fluid velocity by using high-frequency sound waves. They operate by transmitting and receiving ultrasonic pulses through the fluid and calculating flow rate based on the time it takes for the sound waves to travel. These meters are non-invasive, highly accurate, and suitable for various liquids, including those with particulates. They come in two main types: Doppler and transit-time, each optimized for specific fluid characteristics. Ultrasonic flowmeters are favored for their minimal pressure drop, low maintenance, and versatility in handling a wide range of flow rates and pipe sizes.
Can Ultrasonic Flow Meter Measure Air Flow?
Yes, ultrasonic flow meters can measure air flow, although the specific design and technology may vary compared to those used for measuring liquid flow. Ultrasonic flow meters for gases, including air, typically utilize the transit-time differential method, which is highly effective for measuring the flow rate of gases.
How It Works for Air Flow
When measuring air flow, the ultrasonic flow meter operates on the same basic principle as it does for liquids. It uses the difference in the transit time of ultrasonic pulses traveling with and against the flow direction to determine the velocity of the air moving through the pipe or duct. Here’s a simplified explanation:
Transit-Time Measurement: The flow meter has two ultrasonic sensors positioned a known distance apart on the pipe or duct carrying the air. One sensor emits an ultrasonic pulse that travels downstream with the flow of air, while the other sensor emits a pulse that travels upstream, against the flow.
Time Difference Calculation: The time it takes for each pulse to reach the opposite sensor is measured. The pulse moving with the flow of air will arrive sooner than the one moving against the flow. The difference in these transit times is directly proportional to the velocity of the air flow.
Flow Rate Calculation: Once the velocity of the air is known, the flow meter can calculate the flow rate by incorporating the cross-sectional area of the pipe or duct.
Considerations for Air Flow Measurement
Gas Properties: The accuracy of ultrasonic flow meters for gases can be influenced by the acoustic properties of the gas, such as sound speed, which can vary with temperature, pressure, and composition. Therefore, high-quality ultrasonic flow meters for air or gas often incorporate temperature and pressure compensation to maintain accuracy under varying operating conditions.
Calibration: For the highest accuracy, especially in critical applications, ultrasonic flow meters may need to be calibrated specifically for the type of gas and the range of operating conditions expected.
Applications: Ultrasonic flow meters for air are used in various applications, including HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, compressed air systems, and in industries where precise control of gas flow is essential, such as in chemical processing, power generation, and research laboratories.
In summary, ultrasonic flow meters are capable of accurately measuring air flow by utilizing the transit-time method, with considerations made for the specific properties and conditions of gas flow measurement. Their non-intrusive nature, lack of moving parts, and ability to measure flow in both directions make them an attractive choice for many air flow measurement applications.
How Do Ultrasonic Flowmeters Work?
Ultrasonic flowmeters measure the velocity of a fluid with ultrasound to calculate volume flow. They work by sending high-frequency sound waves across the fluid flow path and measuring how those sound waves are affected by the flowing fluid. The operation of ultrasonic flowmeters can be categorized into two primary types based on their measurement technique: Transit-Time (Time-of-Flight) and Doppler shift. Here's how each type works:
1. Transit-Time (Time-of-Flight) Ultrasonic Flowmeters
Transit-Time flowmeters are the most common type of ultrasonic flowmeter. They operate based on the principle that the speed of an ultrasound wave traveling through a fluid is affected by the direction of the fluid flow. In simple terms, sound waves traveling in the direction of the fluid flow move faster than those traveling against it. The flowmeter uses this principle by sending ultrasonic pulses through the fluid in both directions.
2. Doppler Shift Ultrasonic Flowmeters
Doppler Shift flowmeters are used for fluids that contain suspended particles or bubbles, which are necessary for the Doppler effect to occur. These flowmeters measure the change in frequency of the ultrasonic wave as it reflects off particles or gas bubbles within the fluid.
Advantages and Applications
Ultrasonic flowmeters are highly versatile and offer several advantages, including:
Non-intrusive measurement: They do not require any moving parts to be inserted into the fluid, minimizing maintenance and pressure drop.
Wide range of applications: Suitable for clean, dirty, or aerated liquids and gases.
High accuracy and repeatability: Especially transit-time flowmeters, which are highly accurate for clean, particulate-free fluids.
These flowmeters are used in various industries, including water and wastewater, oil and gas, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries, for both control and custody transfer applications.
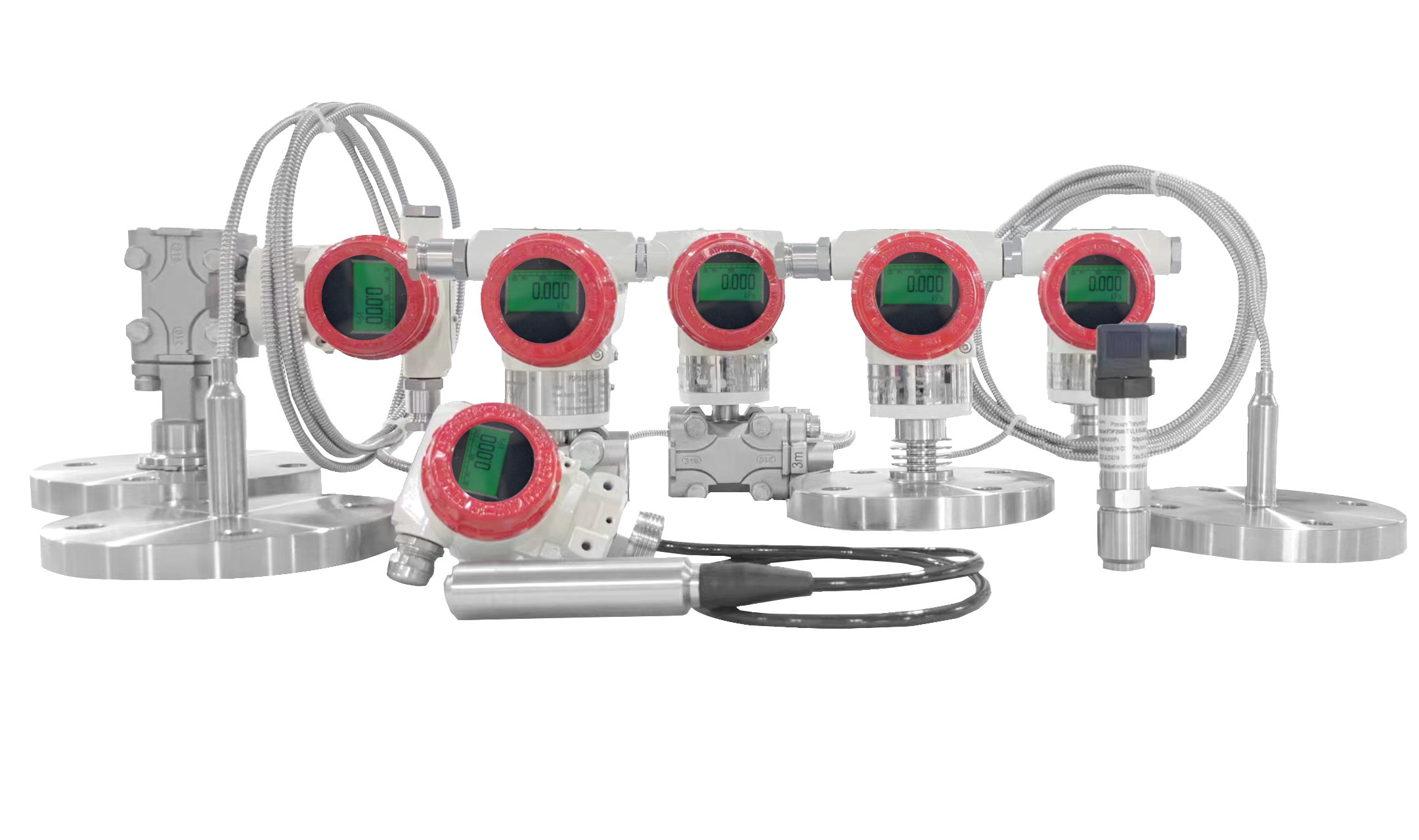
 Smart Pressure Transmitters
Smart Pressure Transmitters